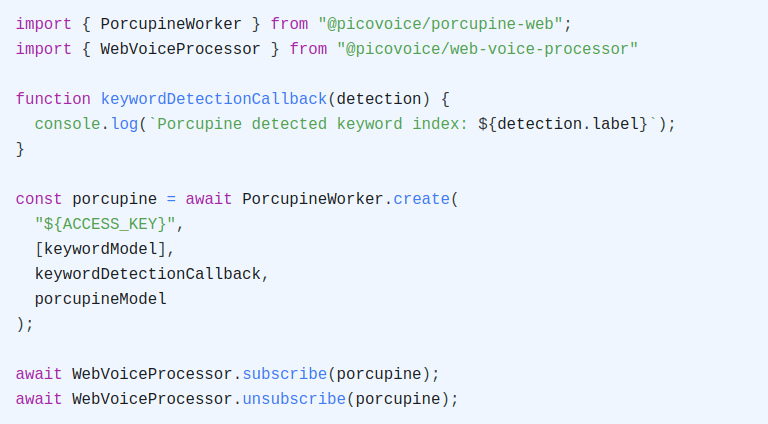
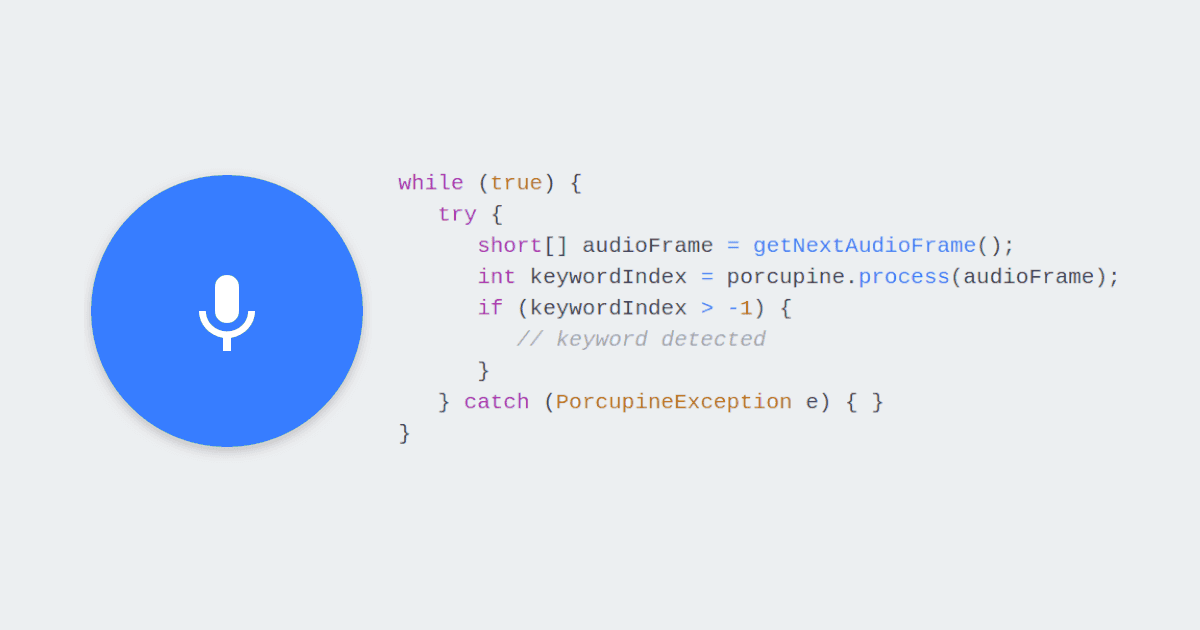
Cloud computing has been the driving force in the adoption of voice AI, but it has inherent limitations due to its reliance on connectivity. Edge computing can address these shortcomings by complementing the cloud or even eliminating it as a dependency. Edge voice AI respects user privacy, incurs minimal latency, and provides superior reliability. On-device processing facilitates building context-aware and power-efficient voice interfaces that are cost-effective at scale.
Over the last decade, a trend in user interfaces transformed the architecture of web applications, shifting functionality from servers to browsers. This has assisted in building applications that are responsive, context-aware, and scalable. Recent advances in IoT hardware and AI algorithms could signal the start of a similar trend in building better voice interfaces. Shifting voice recognition and natural language understanding from the cloud to the edge can offer the following benefits:
Privacy
With increasing user privacy concerns and regulations (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.), performing natural language understanding using a cloud-based provider may not be a viable option. Uploading personal voice recordings is especially risky in data-sensitive applications such as healthcare and finance.
Latency
In voice user interfaces (VUIs), milliseconds of delay matter. Responsiveness is crucial in TV, AR and VR applications, where voice is used as the primary method of interaction.
Reliability
Relying on the cloud for voice processing necessitates continuous Internet connectivity. Even straightforward voice interactions, like asking Siri for the time of the day, requires an Internet connection. In many applications, such as automotive, fickle Internet access can disrupt the user experience.
Efficiency
On battery-powered devices, Internet access is a major power drain due to radio activity (especially on LTE and WiFi).
Cost
Cloud computing is not the affordable option in the long term. At the time of writing, Google DialogFlow and Amazon Lex charge $0.004 per API call [1] [2], which amounts to $14.60 per annum for a voice-enabled device with 10 voice interactions per day. This unbounded operating cost can be prohibitive for device builders. Edge processing can tap into freely-available on-device compute resources to significantly reduce or eliminate cloud and connectivity expenses.
Picovoice provides voice AI on the edge with on-device speech recognition and natural language understanding software. Picovoice software can run on virtually any platform, from microcontrollers to web browsers. Picovoice supports mobile platforms, desktop operating systems (Linux, Mac, Windows), and embedded platforms such as Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone.