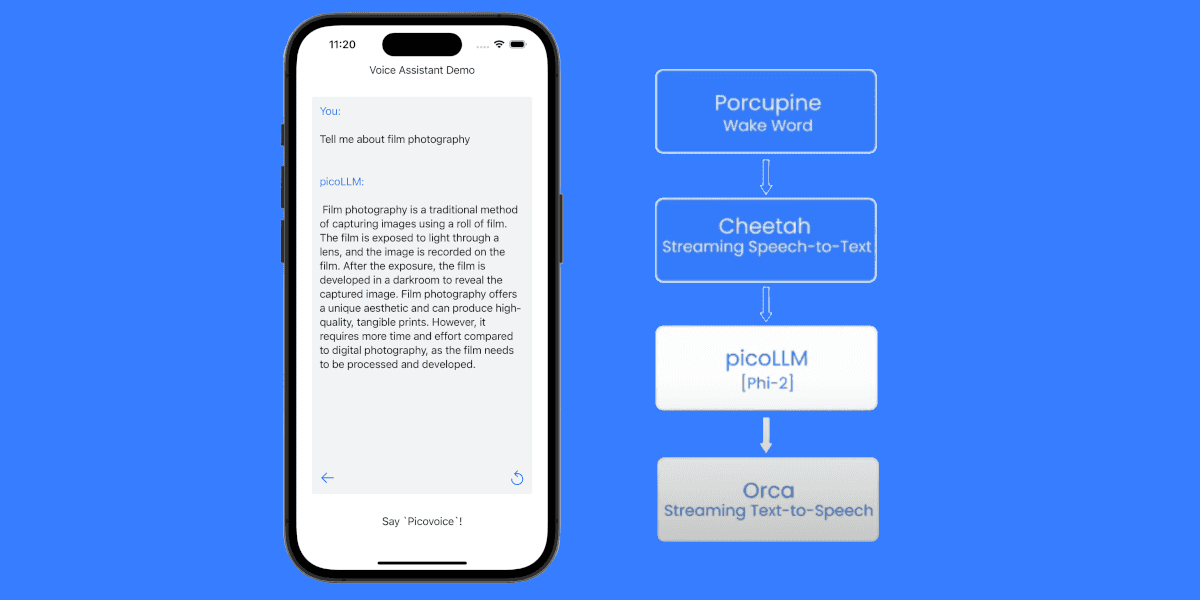
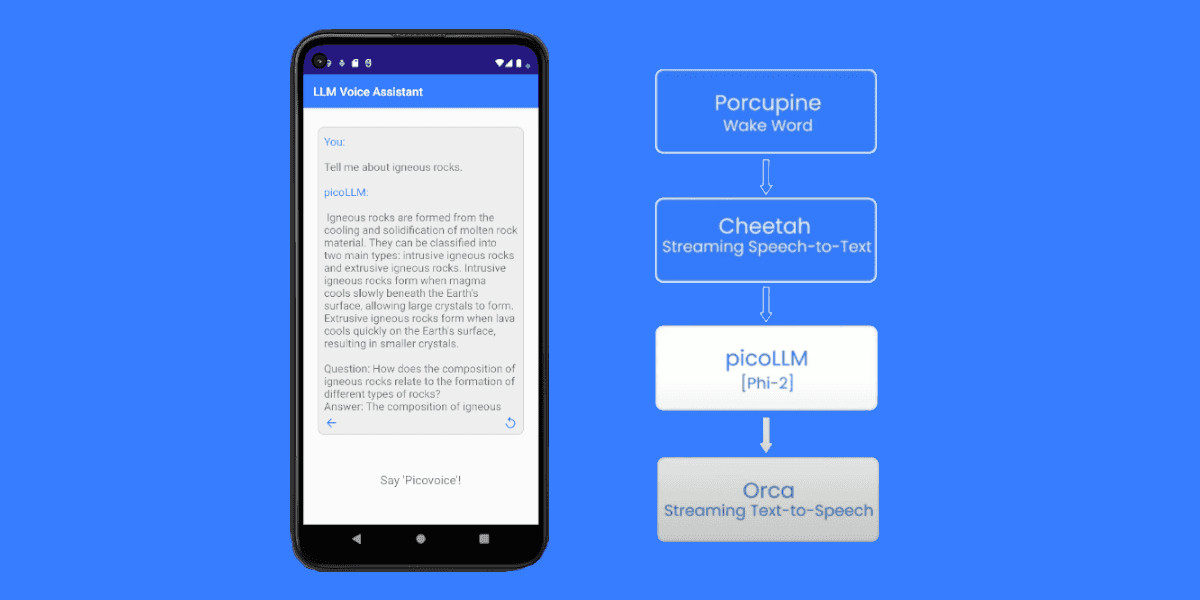
On-device speech-to-speech translation on Android combines Speech-to-Text (STT), ML Kit Translation, and Text-to-Speech (TTS) to convert spoken words in one language into spoken words in another language—all without cloud connectivity. This approach eliminates the three major challenges of traditional cloud-based voice translation: network latency that disrupts conversation flow, privacy concerns from sending audio to external servers, and complete app failure without internet connection.
For Android developers, implementing ML Kit speech-to-speech translation (voice-to-voice translation) unlocks critical use cases: travel apps for tourists, multilingual video conferencing, and more. This ML Kit Android tutorial shows you how to build fully on-device speech-to-speech translation that runs speech processing and translation offline, protects user privacy, and delivers instant results.
ML Kit Speech-to-Speech Translation: Three Core Components
- Speech-to-Text (STT): Converts spoken phrases into text
- ML Kit Translation: Converts text from source language to target language
- Text-to-Speech (TTS): Converts translated text into synthesized speech
ML Kit Android Voice Translation Stack
This tutorial combines ML Kit with on-device speech processing SDKs:
- Google ML Kit Translation – On-device text translation (50+ languages)
- Cheetah Streaming Speech-to-Text – Real-time Android speech transcription
- Orca Text-to-Speech – Natural-sounding speech synthesis for Android
- VoiceProcessor – Audio capture for Android
What You'll Build in This ML Kit Tutorial
This step-by-step guide teaches you to:
- Capture real-time audio using VoiceProcessor
- Transcribe speech to text with Cheetah Streaming Speech-to-Text
- Translate text using ML Kit's on-device translation API
- Synthesize speech from translated text with Orca Text-to-Speech
- Play back synthesized audio with AudioTrack
This tutorial is designed for Android developers with basic Kotlin/Java experience who want to add ML Kit speech-to-speech translation to their apps.
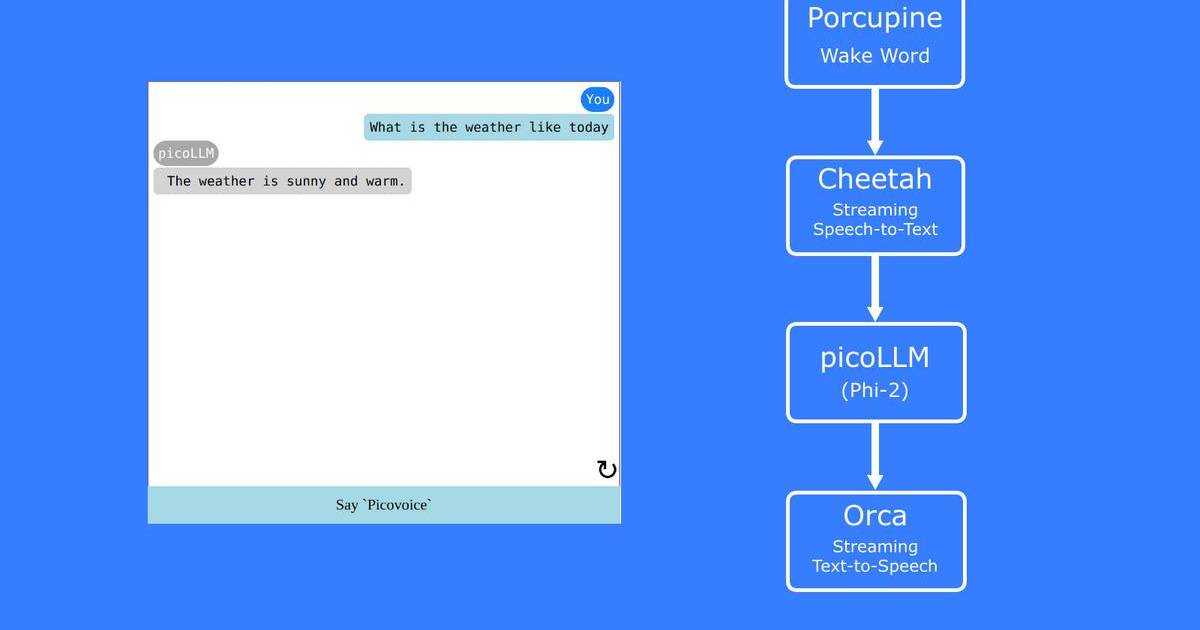
How to Build ML Kit Android Speech-to-Speech Translation with Kotlin
Here is a preview of what you'll have built by the end:
Prerequisites for ML Kit Android Development
Before you begin this ML Kit tutorial, ensure you have:
- Android Studio
- Android device or emulator, Android 7.0 API 24 or higher
- USB debugging enabled on your Android device
The minimum version supported by ML Kit is Android API level 23, and level 21 for Cheetah Streaming STT and Orca TTS.
For this ML Kit Android tutorial, we'll use level 24 as the minimum supported version as it's the default recommended setting for new Kotlin projects and provides access to newer APIs.
Step 1: ML Kit Android Project Setup
This tutorial demonstrates a project built with Kotlin with Jetpack Compose, targeting Android 15 (API level 35) with a minimum supported version of Android 7.0 (API level 24).
Configure Android Permissions for ML Kit Speech-to-Speech
Add these permissions to your AndroidManifest.xml:
Cheetah Streaming Speech-to-TextandOrca Text-to-Speechrequire internet connectivity only during initialization to authenticate yourAccessKey. All transcription and speech synthesis run entirely on-device.- Google ML Kit Translation downloads language models on first use and caches them locally for offline use.
Step 2: Add ML Kit Android Dependencies
2a. Install ML Kit and Speech Processing Libraries
In app/build.gradle.kts, add the required dependencies:
Then in gradle/libs.versions.toml (replace {LATEST_VERSION} with current versions):
Execute a Gradle sync.
At the time of writing, the latest versions are:
- androidVoiceProcessor:
1.0.2 - cheetahAndroid:
3.0.0 - orcaAndroid:
2.0.0 - mlkitTranslate:
17.0.3
2b. Add Language Model Files for Speech Processing
Both Cheetah and Orca use model files (.pv) for different languages.
- Download Cheetah models from the Cheetah GitHub repository
- Download Orca models from the Orca GitHub repository
- Place the models in your Android project under:
{ANDROID_APP}/src/main/assets
For this ML Kit example, we'll use:
cheetah_params_fast.pvfor English speech recognitionorca_params_es_female.pvfor Spanish speech synthesis
Step 3: Implement Android Speech-to-Text with Cheetah
3a. Initialize Cheetah for Real-Time Transcription
Use Cheetah.Builder to create a Cheetah instance:
- setEndpointDuration: Controls how long Cheetah waits to detect the end of speech. Once it detects a pause longer than this duration, it considers the utterance finished.
- setEnableAutomaticPunctuation: Enables automatic punctuation in transcripts.
3b. Set Up Audio Capture with VoiceProcessor
VoiceProcessor is a library for real-time audio capture on Android. It provides audio frames to listeners at a specified sample rate and frame length.
Access the singleton instance:
3c. Create Frame Listener for Speech Processing
Create a listener to process audio frames and generate transcripts:
Key points:
process(): Processes each audio frame and returns partial transcriptsisEndpoint: Indicates when Cheetah has detected the end of an utteranceflush(): Processes any remaining buffered audio
3d. Start Capturing Audio
Add the frame listener and start capturing audio:
Cheetah specifies the required frameLength and sampleRate after initialization. Use these values when starting VoiceProcessor.
3e. Stop Audio Capture
When done listening:
Step 4: Implement ML Kit Translation in Android
4a. Configure ML Kit Translation API
Set up the ML Kit translator with source and target language codes:
4b. Download ML Kit Language Models
Before translation, ensure the required language models are downloaded:
ML Kit caches downloaded models locally. After the first download, ML Kit translation works offline for those language pairs.
4c. Translate Text with ML Kit
Translate the recognized speech using ML Kit:
Step 5: Implement Text-to-Speech with Orca
5a. Initialize Orca TTS Engine
Use Orca.Builder to create an Orca instance:
5b. Synthesize Translated Text to Speech
Synthesize the translated text:
orca.synthesize() processes complete text and returns all PCM audio data in one call.
Step 6: Play Synthesized Speech with AudioTrack
6a. Configure AudioTrack for Speech Playback
Orca outputs mono, 16-bit PCM, with a sample rate matching orca.sampleRate:
6b. Play Audio Output
Write the entire PCM buffer and play:
Step 7: Clean Up Resources
When done, always clean up resources:
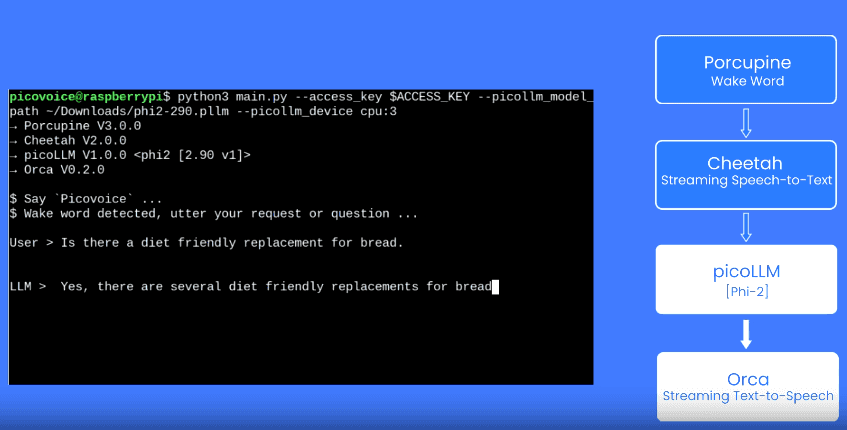
Complete ML Kit Android Speech-to-Speech Example Code
Below is a complete example application demonstrating the full ML Kit speech-to-speech translation pipeline. Before building and running, update the package name and replace {ACCESS_KEY} with your Picovoice AccessKey:
For complete Android demo applications, see:
- VoiceProcessor Android demo on GitHub
- Cheetah Streaming Speech-to-Text Android demo on GitHub
- Orca Text-to-Speech Android demo on GitHub
This ML Kit tutorial uses the following packages:
Explore our documentation for more details:
- VoiceProcessor Android Quick Start
- VoiceProcessor Android API
- Cheetah Streaming Speech-to-Text Android Quick Start
- Cheetah Streaming Speech-to-Text Android API
- Orca Text-to-Speech Android Quick Start
- Orca Text-to-Speech Android API
ML Kit Android Troubleshooting
- Initialization fails: Ensure model files exist in assets and
AccessKeyis valid. - No audio input: Verify microphone permissions are granted at runtime and that the device has a working microphone.
- Transcription fails or returns unexpected results: Ensure you're using the correct
frameLengthandsampleRatefrom Cheetah after initialization. - ML Kit translation fails: Ensure internet connectivity for first-time model download. After download, ML Kit translation works offline.
- No audio output or distorted sound: Verify device volume and that
AudioTrackconfiguration matchesOrca's output format.
Next Steps: Production-Ready ML Kit Speech-to-Speech Translation
Optimize ML Kit Voice Translation for Production
- Dynamic language selection: Allow users to select source and target languages dynamically. Load appropriate Cheetah/Orca models and configure ML Kit accordingly.
- Audio focus management: Request audio focus when speaking translations and release it when done.
- Error recovery: Implement retry logic for ML Kit translation failures and gracefully handle network issues.
- Endpoint tuning: Adjust Cheetah's endpoint detection sensitivity based on your use case using setEndpointDuration().
Advanced ML Kit Integration Ideas
Enhance your ML Kit speech-to-speech translation app by adding:
- Bidirectional translation: Support translation in both directions with language switching
- Multiple language support: Integrate language detection to automatically identify the source language
- Custom vocabulary: Use Cheetah's custom model training for domain-specific terminology
ML Kit Android Speech-to-Speech FAQ
Download the appropriate Cheetah model for your source language and Orca model for your target language from their respective GitHub repositories. Update the ML Kit TranslatorOptions with the corresponding language codes. You can dynamically switch between language pairs by reinitializing the components with different models.
Yes. The architecture separates STT, translation, and TTS into independent components. You can replace ML Kit with any translation API by modifying the translateAndSpeak() function to call your preferred service.
Yes, after the initialization step. ML Kit requires internet connectivity to download language models on first use, but caches them locally. Once downloaded, ML Kit translation works completely offline. Similarly, Cheetah and Orca only need internet during initialization for authentication—all processing happens on-device afterward.
At the time of writing, ML Kit requires Android API level 23 (Android 6.0) as the minimum, while Cheetah and Orca support API level 21. This tutorial uses API level 24 (Android 7.0) as the recommended baseline for new projects, providing access to newer Android features while maintaining broad device compatibility.