To run language models locally in .NET, developers typically rely on open-source options like llama.cpp bindings or ONNX Runtime. While these work for prototyping, they hit production roadblocks as they require managing external processes, handling runtime dependencies, and manually optimizing models for deployment.
This tutorial shows a simpler path: add local LLM inference to your .NET application in minutes using the picoLLM .NET SDK. You'll build a working C# application with straightforward NuGet package installation, simple API calls, and reliable cross-platform deployment. No manual model quantization or optimization, no compatibility issues, no cloud processing.
Setting Up the .NET LLM Inference API
This walkthrough shows you how to run local LLM inference in .NET without cloud APIs. You'll install picoLLM, load a quantized model, and generate text entirely on-device.
Prerequisites for .NET Local LLM Integration
- Windows (x86_64): .NET Framework 4.6.1+, .NET Standard 2.0+, or .NET Core 3.0+
- macOS (x86_64): .NET Standard 2.0+ or .NET Core 3.0+
- macOS (arm64), Windows (arm64), Linux (x86_64), Raspberry Pi (4, 5): .NET 6.0+
Step 1: Install the .NET On-Device LLM Package
Add the official PicoLLM NuGet package to enable local LLM inference in your C# project:
Step 2: Download a Quantized LLM Model File
Sign up for a Picovoice Console account (free tier available) and copy your AccessKey from the dashboard.
Download a .pllm model file from the picoLLM page. For this tutorial, choose a model with chat support (e.g., Llama 3.2, Phi-2, Phi-3, Phi-3.5).
Step 3: Initialize the Local LLM Inference Engine in C#
Create an instance of picoLLM with your AccessKey and path to the downloaded model:
Step 4: Create a Dialog for Conversational Context
Use PicoLLMDialog to manage multi-turn conversations:
The dialog object maintains conversation history, so the model can reference previous messages. For single-turn generation (no conversation context), you can pass prompts directly to Generate() instead:
Step 5: Configure Text Generation Parameters
Control inference behavior with parameters that affect output randomness, length, and repetition:
Parameter guide:
temperature: Lower values make output more deterministiccompletionTokenLimit: Maximum number of tokens to generatepresencePenalty/frequencyPenalty: Reduce repetition
See the picoLLM API docs for the complete parameter list.
Step 6: Generate Text with Streaming Output
Stream tokens as they're generated instead of waiting for the complete response:
Streaming allows you to display output progressively as it's generated rather than waiting for the complete response.
Interrupt generation mid-stream if needed (e.g., user cancels or types a new message):
Step 7: Clean Up .NET LLM Resources
Free memory immediately after use by wrapping in a using statement:
Or call Dispose() manually when done. Without explicit disposal, the GC will eventually free resources.
Complete C# Example: .NET On-Device LLM Chat Application
Here's a working console app implementing local LLM inference with conversation history, streaming, and interruption handling:
This example includes the core functionality you need: model initialization, conversation management, streaming output, and interrupt handling. For a more complete implementation with error handling and advanced features, see the picoLLM .NET demo on GitHub.
Tips & Best Practices: LLM Inference in .NET
- Prompt clarity: Provide clear and concise prompts to get the best results.
- Context management: Keep track of conversation state for multi-turn interactions. If you're using
picoLLM LLM Inference, you can configure this with thehistoryparameter of GetDialog. - Choosing the right chat template: Some models define multiple chat template modes. For example,
phi-2allows bothqaandchattemplates. Set the mode you wish to use in GetDialog for the best results. - Resource efficiency: Dispose of LLM instances when not needed to minimize memory use.
Troubleshooting .NET Local LLM Issues
Model Load Failures
Verify the .pllm file path is correct and file exists. Check that the file isn't corrupted (re-download if needed).
Performance bottlenecks
Common bottlenecks include large prompt histories, oversized models, or running multiple inference sessions simultaneously on limited-core devices. Monitoring CPU and memory usage during runtime can help identify which part of your workflow is slowing down. Consider limiting context length or using lighter models for faster responses.
Incorrect or unexpected responses
If the model produces irrelevant or confusing output, check your prompt clarity and context history. Overly long or ambiguous prompts can confuse the model. Trimming unnecessary conversation history or refining prompts can improve response quality.
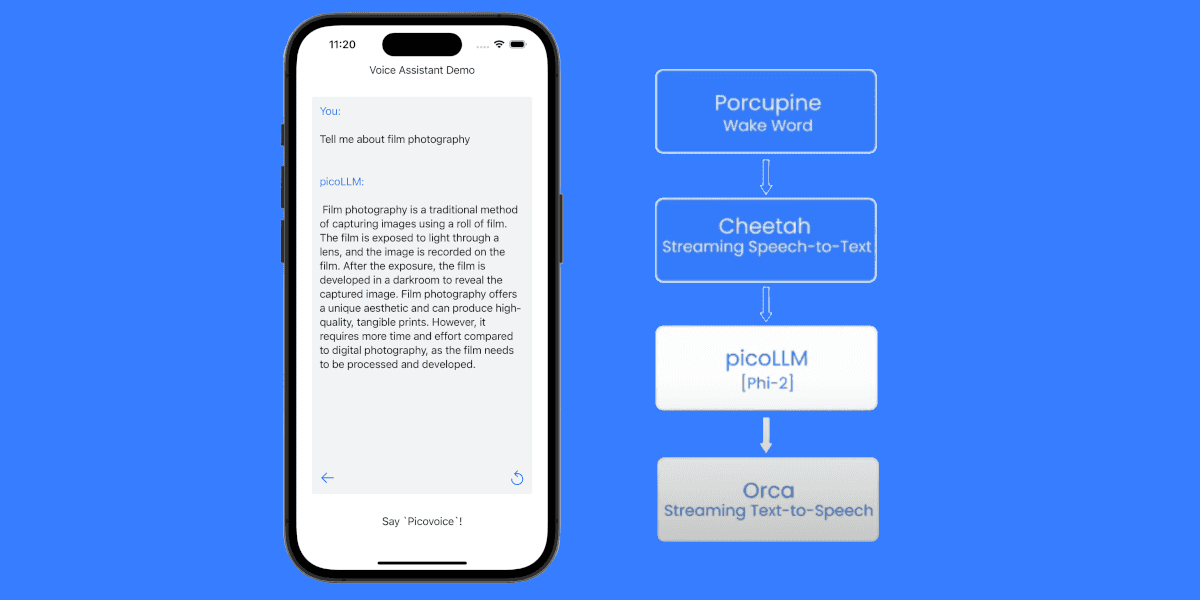
Building Voice-Enabled .NET Applications with Local LLMs
Combine picoLLM with speech engines to build fully voice-controlled applications:
Complete voice assistant stack:
- Porcupine Wake Word: Activates the assistant using a custom phrase such as "Hey Assistant"
- Cheetah Streaming Speech-to-Text: Captures the user's spoken prompt and displays transcribed text in real time
- picoLLM: Interprets the prompt and generates a response
- Orca Text-to-Speech: Streams the generated response back to the user as speech
All of these run on-device with no cloud dependencies. See the complete implementation in the .NET LLM Voice Assistant demo on GitHub.
Use cases:
- Offline voice assistants for desktop apps
- Privacy-focused enterprise tools (no data leaving corporate network)
- Embedded devices with limited internet (kiosks, industrial equipment)
.NET On-Device LLM Documentation and Resources
Official packages and docs:
Models and usage management:
- Picovoice Console: download optimized models
Frequently Asked Questions: Local LLMs in .NET
On-device LLM inference allows a .NET application to run a local language model for text generation or chat without relying on cloud APIs. This ensures low latency, predictable performance, and full data privacy.
picoLLM works on Windows, macOS, Linux, and Raspberry Pi (x86_64 and ARM64), supporting desktop, mobile, and embedded .NET applications.
Once the model is downloaded, all processing happens locally on your device. Internet is required only for licensing and usage tracking.
Yes. By using the PicoLLMDialog object, you can manage conversation history and maintain context across multiple prompts and responses.