Modern voice applications need more than transcripts. Our voice data carries cues about turn-taking, speaker changes, and identity that text alone does not capture. For example, a meeting recap is more effective when it indicates "who spoke when", and a hands-free login is more secure when it recognizes "who is speaking". These are required in speech analysis for searchability, compliance, access control, and personalization.
Speaker Diarization and Speaker Identification are two powerful voice analytics technologies that help accurately extract this speaker information from audio. While both identify different speakers in speech, they serve distinct purposes and are essential components of modern speech-to-text pipelines. Understanding the difference between Speaker Diarization and Speaker Identification is essential for building effective multi-speaker audio analysis systems, whether you're developing meeting transcription software, call center analytics, or voice authentication platforms.
What is Speaker Diarization?
Also known as speaker separation or speaker tracking, Speaker Diarization answers the question “who spoke when?” in multi-speaker audio such as meetings, interviews, podcasts, or conference calls. Speaker Diarization segments audio samples by speaker without requiring any prior knowledge of who the speakers are. Instead of identifying individuals by name, it assigns speaker labels like Speaker 1, Speaker 2, and so on. When combined with speech-to-text engines, it makes transcripts more readable and analyzable by organizing the conversation flow. This is valuable for both human readers and machines that need to understand conversational context.
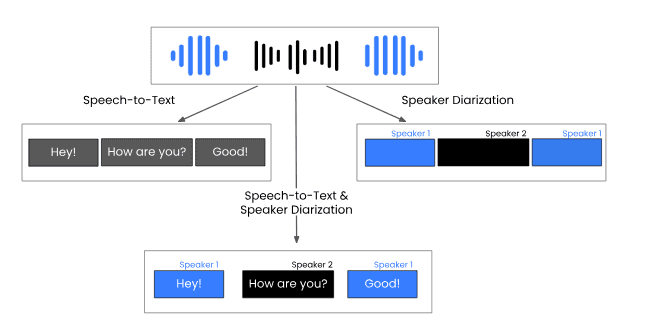
The diagram above shows how speech-to-text engines produce blocks of text, and Speaker Diarization splits the audio into speaker-specific segments for clarity.
Key Use Cases for Speaker Diarization:
Speaker Diarization powers applications across industries where speaker attribution improves analysis and documentation:
- Meeting Transcription: Use
Speaker Diarizationfor meeting transcription software to provide accurate speaker attribution in business conversations. - Media & Broadcasting: Automatically assign speaker labels in podcast transcriptions, live broadcast captioning, and interview archiving.
- Call Center Analysis: Separate agent and customer speech for quality monitoring for customer service calls.
- Healthcare Documentation: Segment speakers in medical consultations, team rounds, and telehealth appointments to organize clinical notes and create compliant medical transcripts.
What is Speaker Identification?
Speaker Identification is a branch of speaker recognition that determines "who is speaking?" through voice authentication. It compares an incoming voice sample against a set of known speaker profiles or enrolled speaker IDs. Speaker Identification compares the acoustic characteristics of speech to pre-enrolled voice prints and returns the confidence scores for each enrolled speaker ID. Confidence scores are probability values between 0.0 and 1.0, where higher scores indicate a stronger match. For example, a score of 0.87 suggests high confidence that the speaker is talking, while 0.15 indicates they likely are not.
Key Use Cases for Speaker Identification:
Speaker Identification enables secure, personalized experiences across various applications:
- Security & Access Control: Identify authorized users by voice authentication for banking apps, smart devices, and secure facility access.
- Personalization: Customize smart home settings, app preferences, and content recommendations based on identified speakers.
- In-Vehicle Systems: Detect the driver's voice to automatically adjust seat position, mirror angles, climate control, and infotainment settings.
- Forensic Analysis: Match recorded voices to known speakers for voice biometrics of suspects or witnesses in legal investigations.
What is the difference between Speaker Diarization and Speaker Identification?
Speaker Enrollment Requirements
Speaker Diarization: No enrollment needed. Works immediately on any multi-speaker audio without prior voice samples.Speaker Identification: Requires speakers to register voice prints in advance. Cannot identify speakers who haven't been enrolled.
Output Format
Speaker Diarization: Returns time-stamped segments with speaker labels.
Speaker Identification: Returns confidence scores for each enrolled speaker ID, indicating how closely the detected voice matches each registered voiceprint.
Cross-File Consistency
Speaker Diarization: Speaker labels don't persist across files. Speaker 1 in Recording A may be a completely different person than Speaker 1 in Recording B.Speaker Identification: Speaker identities remain consistent. Jane Doe will always be recognized as Jane Doe across all audio files, regardless of when or where the audio comes from.
Can You Use Speaker Diarization and Speaker Identification Together?
Yes! Many voice analytics systems combine both technologies for the most accurate and comprehensive multi-speaker analysis. In a conversation or meeting, Speaker Diarization detects when different people are speaking, while Speaker Identification determines who those speakers are.
Speaker Diarization first separates the audio into segments based on who is speaking when, even if the system doesn’t know their identities in advance:
Once the audio is segmented, Speaker Identification compares each segment to enrolled speaker IDs to assign identities where the speakers are known:
When all participants are enrolled, every segment can be mapped to a known speaker ID. If new or unenrolled voices appear, they remain generically labeled while the rest are identified. This combined workflow ensures that diarization captures every speaker turn, while identification adds speaker-specific context to each segment.
Together, they deliver transcripts that are structured, searchable and identity-aware, making them ideal to transcribe online meetings, interviews, and any multi-speaker environment.
Get Started with Picovoice
Ready to implement speaker analysis in your application? Picovoice offers production-ready solutions for both technologies:
- Eagle Speaker Recognition: Picovoice’s engine for
Speaker Identification, enabling secure voice authentication and personalized user experiences. - Falcon Speaker Diarization: Segment multi-speaker audio on-device with speaker labels for speaker-attributed transcripts.
With Picovoice Falcon Speaker Diarization and Eagle Speaker Recognition, you can process audio entirely on-device, eliminating cloud dependencies and privacy concerns while delivering highly accurate performance.
Not sure which solution fits your use case? Our experts can help you choose the right approach.
Consult an Expert