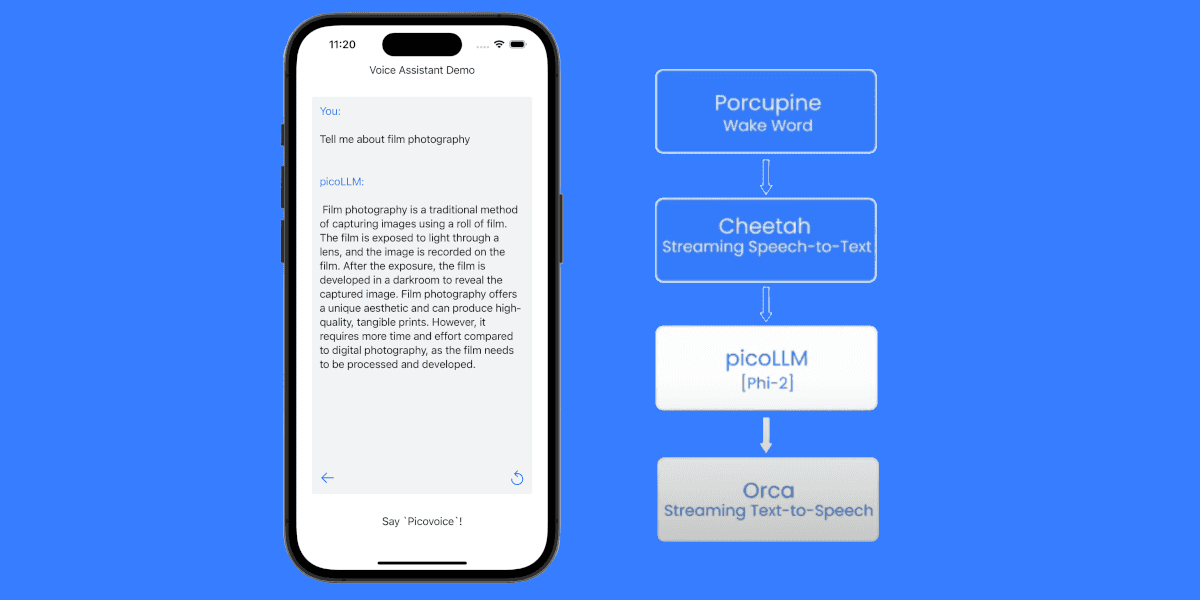
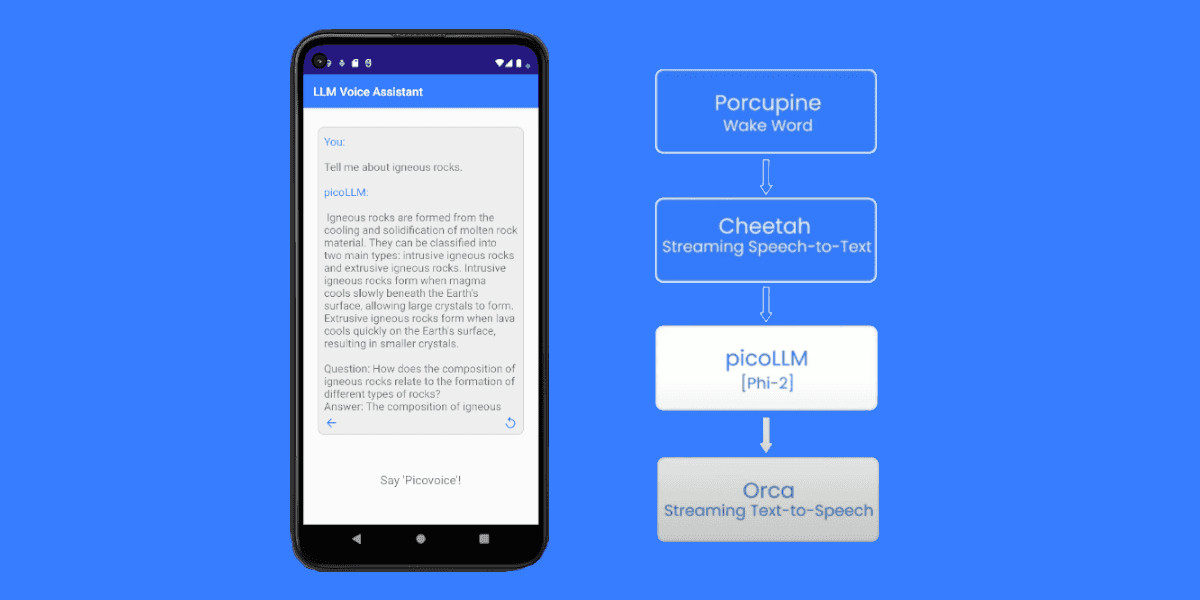
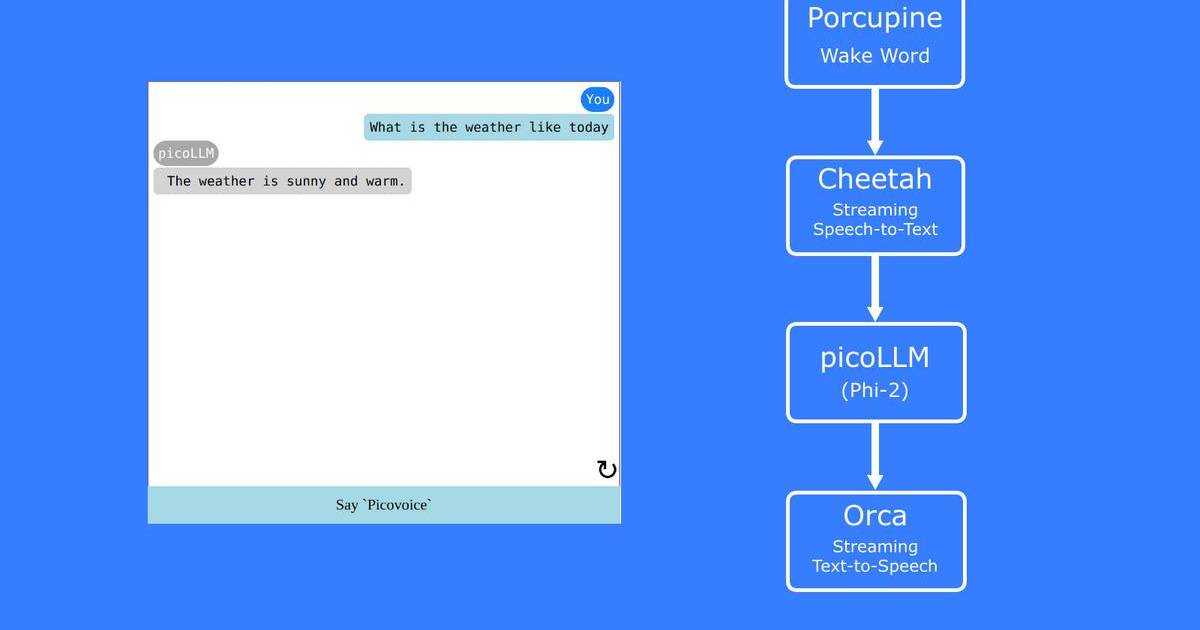
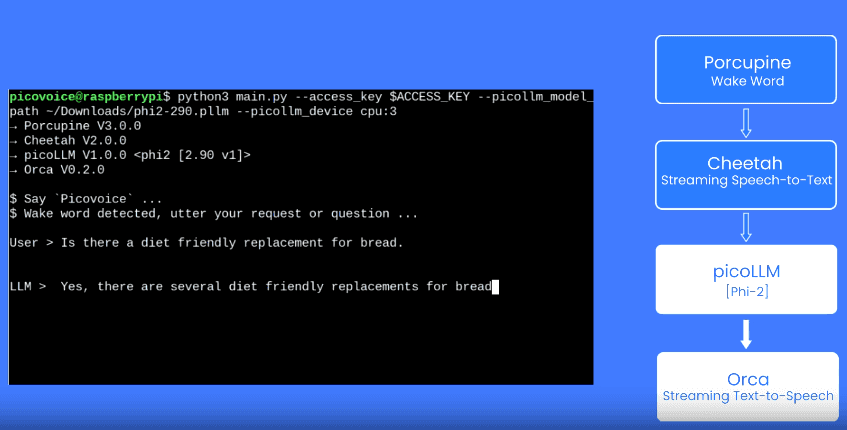
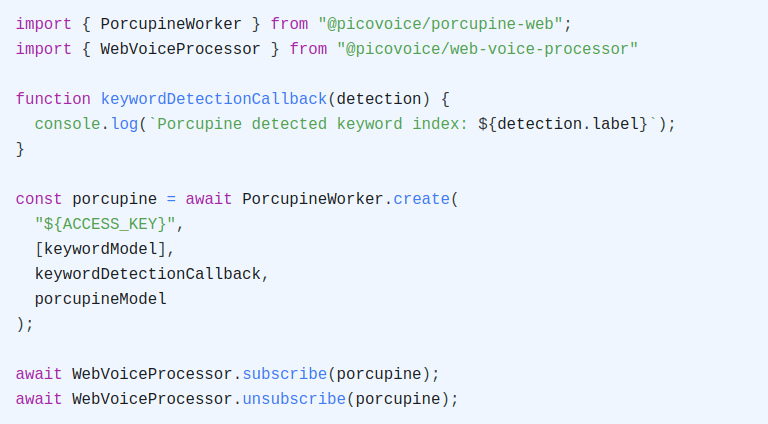
From AI agents and real-time coaching to meeting transcription, speech-to-text brings new ideas to life. Cheetah Streaming Speech-to-Text has created even more opportunities with cloud-level accuracy on the device in real time, combining the best of the cloud and on-device processing.
Now, Cheetah Streaming Speech-to-Text officially supports five new languages: French, German, Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish. More developers can build private and cost-effective AI applications with zero network latency using accurate, production-ready, cross-platform Cheetah Streaming Speech-to-Text.
On-device transcription with cloud-level accuracy within your web browser
Picovoice’s web demos leverage its web SDKs. They run within your web browser, meaning the audio is processed locally without using 3rd party cloud services.
Real-time transcription with Cheetah Streaming Speech-to-Text
Test Cheetah Streaming Speech-to-Text in English or change the language to French, German, Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish to test out the new languages.
Train Use-case Specific Speech Models
Cheetah Streaming Speech-to-Text offers cloud-level accuracy out-of-the-box. However, some use cases and industries, such as healthcare, finance, or legal, have special terminology that cannot be accurately predicted by generic speech models. Custom Vocabulary & Keyword Boosting features allow developers to customize speech-to-text models specific to their application on the no-code Picovoice Console.
Start Building Now
Building with intuitive and cross-platform speech-to-text SDKs doesn’t require any experience in Machine Learning. Anyone can start transcribing with a few lines of code.
o = pvcheetah.create(access_key)partial_transcript, is_endpoint =o.process(get_next_audio_frame())